Speaker
Description
The position sensors are widely used in various industrial applications. The sensors with linear variable differential transformer (LVDT) configuration are the most common position transducers because of their cost-effective and simple structure and straightforward operation. LVDT position sensors are used in robotics, automation, manufacturing and machining processes, automatic valves, and the automotive and aviation industries.
Conventional LVDT position sensors have cylindrical structure with solenoidal coils and moving part and the moving part or armature is a ferromagnetic cylinder. However, the cylindrical LVDT sensors cannot be used for applications, where the armature and the coils must be physically separated. Flat-tape LVDT position sensors [1,2] are alternatives to the cylindrical LVDT sensors, which have more mechanical feasibility for the position measurement. However, achieving high linearity in flat-type position sensors is more challenging.
A novel structure of flat-type position sensors is presented in this paper. Fig. 1 presents the magnetic flux distribution in the 2D model of the proposed position sensor. The sensor has a long excitation coil, and two differentially connected pickup coils wound around a long-length cuboid Ferrite core. The armature is a short-length cuboid Ferrite core. The pickup coils are optimized to enhance the linearity range of the LVDT position sensor. 2D and 3D finite element methods (FEM) are utilized for the design optimization of the position sensor. Finally, detailed measurements are conducted to evaluate the linearity improvement in the optimized flat-type position sensor.
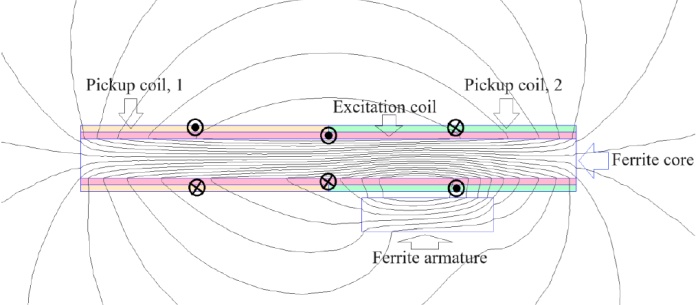
Fig. 1 Magnetic flux distribution in the 2D model of the linear position sensor.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by GACR project 24-12705S Novel Magnetic Position Sensor.
References
[1] Y. Kano, S. Hasebe, and H. Miyaji, “New linear variable differential transformer with square coils,” IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, vol. 26, no. 5. Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), pp. 2020–2022, 1990. doi: 10.1109/20.104605.
[2] M. Mirzaei, J. Machac, P. Ripka, A. Chirtsov, J. Vyhnanek, and V. Grim, “Design of a flat‐type magnetic position sensor using a finite‐difference method,” IET Science, Measurement & Technology, vol. 14, no. 5. Institution of Engineering and Technology (IET), pp. 514–524, Jul. 2020. doi: 10.1049/iet-smt.2019.0197.

